As the population ages, Orthopedic Care for Special Populations becomes increasingly important for managing conditions that impact the mobility and quality of life in older adults. Aging individuals often encounter unique challenges related to bone and joint health, necessitating specialized care and tailored treatment strategies. This blog will delve into the most common orthopedic issues in older adults, effective care methods, available treatment options, and the diagnostic techniques used in orthopedic care for special populations.
What is the Most Common Orthopedic Presentation in Older Adults?

Osteoarthritis is the most common orthopedic condition among older adults. This degenerative joint disease affects millions worldwide and is characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Osteoarthritis often leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. The prevalence of osteoarthritis increases with age, making it a significant concern in orthopedic care for older populations. Additionally, conditions like osteoporosis and fractures due to falls are also common, further emphasizing the need for comprehensive orthopedic care.
What Care Will You Give an Orthopedic Person?
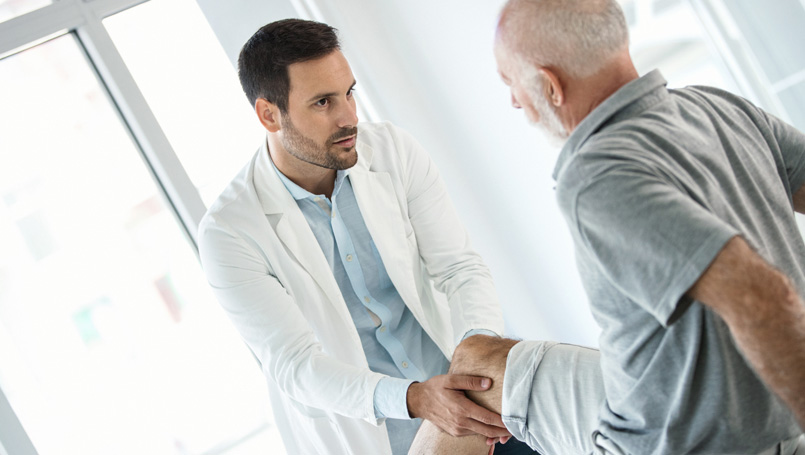

Providing care for an older adult with orthopedic issues requires a multi-faceted approach. First and foremost, pain management is critical. This can be achieved through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In cases of severe pain or disability, surgical interventions such as joint replacement may be necessary.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving mobility. Tailored exercise programs help strengthen muscles around affected joints, reduce stiffness, and improve overall function. Additionally, assistive devices like walkers or canes can provide stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Nutritional support is also essential. A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health and can slow the progression of osteoporosis. Regular monitoring of bone density and other relevant health metrics is necessary to adjust care plans as needed.
How Are Orthopedic Conditions Treated?
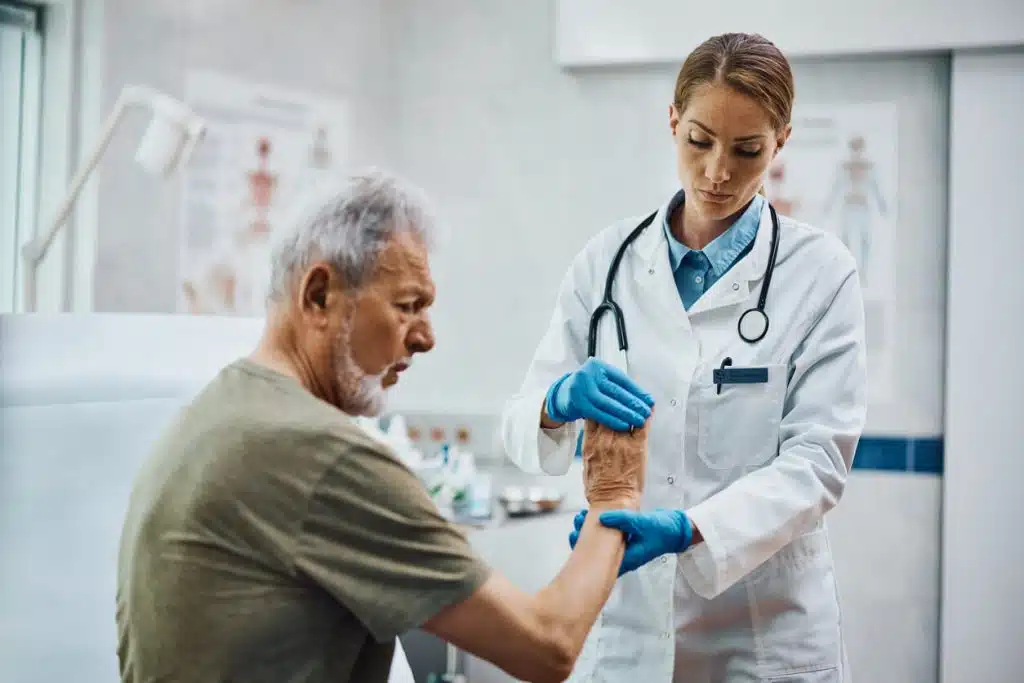

Treatment for orthopedic conditions in older adults typically includes both non-surgical and surgical options, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments often involve medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy is another cornerstone of treatment, helping to maintain or improve joint function through targeted exercises.
For more severe cases, particularly where joint damage is extensive, surgical options may be considered. Joint replacement surgery, such as hip or knee replacement, is a common procedure that can significantly improve quality of life for older adults. Minimally invasive surgical techniques have also become more prevalent, offering quicker recovery times and reduced risks compared to traditional surgery.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle modifications are often recommended. These can include weight management to reduce stress on joints, regular exercise to maintain mobility, and the use of ergonomic furniture or devices to minimize strain on affected areas.
What is the Diagnosis of Orthopedic Conditions Dependent Upon?
Accurate diagnosis is crucial in providing effective orthopedic care. The diagnosis of orthopedic conditions in older adults depends on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Understanding the patient’s history, including the onset and progression of symptoms, is the first step in identifying the condition. Physical examinations help assess the range of motion, strength, and any visible deformities in the joints.
Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans provide detailed views of the bones and joints, allowing for precise diagnosis. For example, X-rays are often used to detect fractures, while MRIs can reveal soft tissue injuries like torn ligaments or cartilage. In some cases, blood tests may be ordered to rule out conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or other inflammatory diseases.
The diagnostic process is also influenced by the patient’s overall health. Age-related factors, such as the presence of multiple chronic conditions, can complicate the diagnosis and treatment plan. Therefore, a comprehensive approach that considers the patient’s entire health profile is essential.
Conclusion
Orthopedic care for older adults requires a specialized approach that addresses the unique challenges of aging. From managing common conditions like osteoarthritis to providing tailored treatments and accurate diagnoses, orthopedic care is critical in preserving mobility and enhancing the quality of life in older populations. By understanding the most common presentations, effective care strategies, treatment options, and diagnostic processes, healthcare providers can ensure that older adults receive the best possible care for their orthopedic needs.
Orthopedic conditions in older adults demand attention and a proactive approach to maintain their independence and well-being. Regular check-ups, physical therapy, and appropriate surgical interventions when necessary, are key components of a comprehensive care plan.
To Know More – Orthopedic Care for Older Adults
