Early detection of bone diseases through orthopaedic screening is crucial for effective management and treatment. Screening can identify bone health issues before they progress to more serious conditions. This article explores bone disease screening, diagnostic tests, bone screening tests, and methods for early detection and preventive treatment of osteoporosis.
What is Bone Disease Screening?
Bone disease screening refers to a set of tests and evaluations designed to identify bone-related health issues early. These screenings aim to detect conditions such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, and other bone disorders before symptoms become severe. Early identification allows for timely intervention and management, which can prevent the progression of bone diseases and improve overall health outcomes.
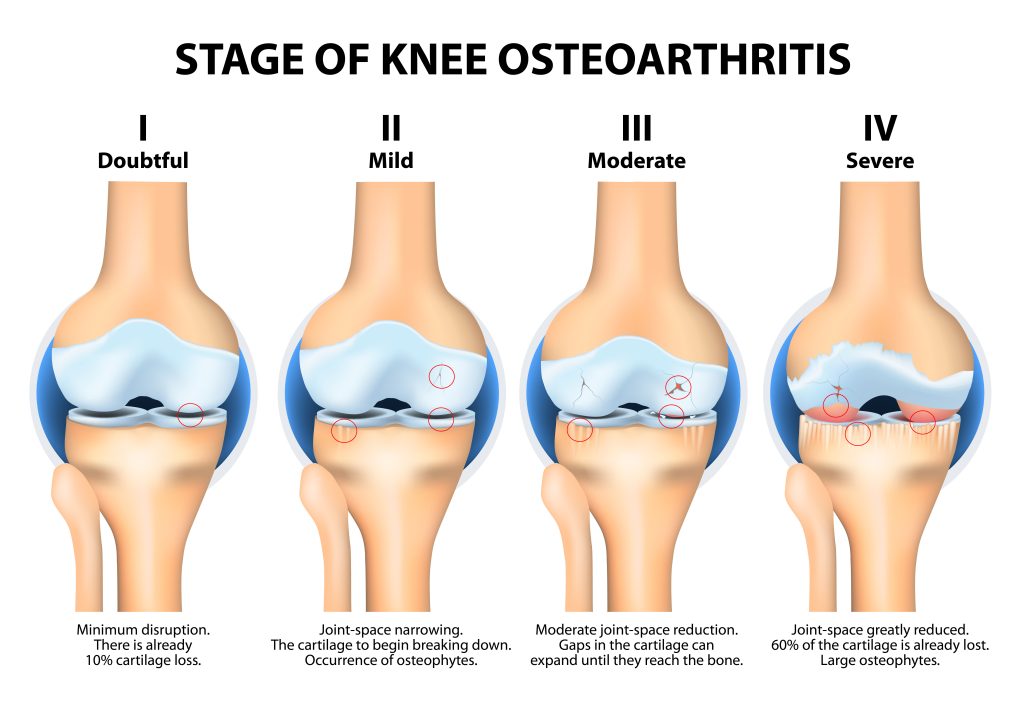
What is the Diagnostic Test for Bone Disease?
The diagnostic test for bone disease varies depending on the specific condition being investigated. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test: This test measures the density of bones using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). It helps diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk.
- X-rays: Standard X-rays can reveal changes in bone structure and detect fractures or deformities. They are often used to assess more advanced bone conditions.
- CT Scans: Computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of bones and are useful for diagnosing complex bone issues.
- MRI Scans: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can show soft tissues and bone marrow changes, helping diagnose conditions like bone tumors or infections.
- Bone Scintigraphy: Also known as a bone scan, this test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material to highlight bone abnormalities, such as infections or tumors.
What is a Bone Screening Test?
A bone screening test is a preliminary assessment used to evaluate bone health and risk factors for bone diseases. The most common bone screening test is:
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): DXA measures bone mineral density (BMD) and is the gold standard for screening osteoporosis. It assesses bone strength and predicts the risk of fractures.
- Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS): QUS evaluates bone density using sound waves. It is often used as a complementary test to DXA.
Bone screening tests help identify individuals at risk of bone diseases and determine the need for further diagnostic testing or preventive measures.
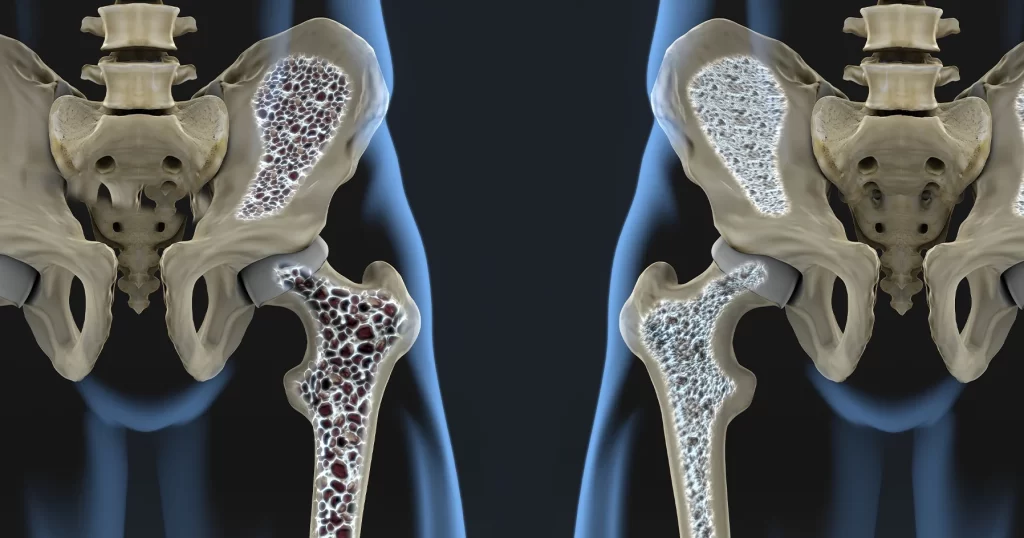
What Test is Used for Early Detection and Preventive Treatment for Osteoporosis?
For early detection and preventive treatment of osteoporosis, the following tests and strategies are commonly used:
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Testing: DXA is the primary test for diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk. It measures BMD at critical sites like the spine, hip, and wrist.
- FRAX® Tool: The FRAX® tool is an online calculator that estimates the 10-year probability of bone fractures based on various risk factors. It helps determine the need for preventive treatment.
- Biochemical Markers: Blood and urine tests can measure biochemical markers of bone turnover. These markers provide information about bone formation and resorption rates.
- Lifestyle and Risk Factor Assessment: Evaluating risk factors such as age, family history, smoking, alcohol use, and physical activity helps in developing a preventive strategy for osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Orthopaedic screening for bone diseases plays a critical role in early detection and management. Bone disease screening involves tests like BMD, X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to diagnose various conditions. Bone screening tests, particularly DXA, are essential for assessing bone health and predicting fracture risk. For early detection and preventive treatment of osteoporosis, BMD testing, the FRAX® tool, biochemical markers, and risk factor assessment are key.
Regular screenings and early intervention can significantly impact the management of bone diseases, reducing the risk of fractures and improving overall quality of life. By understanding and utilizing these screening methods, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining bone health and preventing serious bone conditions.
To Know More What to know about bone diseases
