The gut-brain-bone axis represents a dynamic interconnection between the gastrointestinal system, nervous system, and skeletal health. This complex network underscores the profound impact of gut health on orthopaedic conditions, revealing how digestive well-being influences bone density, joint health, and overall musculoskeletal integrity.
How does gut health affect bone health?
The intricate relationship between gut health and bone health involves several mechanisms crucial for maintaining skeletal integrity:
1. Nutrient Absorption and Bone Mineralization
Active gut microbiota play a pivotal role in enhancing the absorption of essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, which are vital for bone mineralization and strength. Dysbiosis or imbalance in gut flora can hinder this absorption process, potentially contributing to conditions such as osteoporosis.
2. Regulation of Systemic Inflammation
A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate systemic inflammation levels, which is critical for preventing inflammatory bone diseases like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic inflammation can lead to accelerated bone loss and degradation of joint tissues, highlighting the importance of maintaining gut health for musculoskeletal well-being.
What is the role of the gut-brain axis in health and disease?
Understanding the multifaceted role of the gut-brain axis provides insights into its broader implications for overall health and disease prevention:
1. Neural and Hormonal Communication
The gut-brain axis facilitates bidirectional communication between the enteric nervous system of the gut and the central nervous system. This communication influences mood, cognition, and stress responses, underscoring how gut health impacts neurological well-being.
2. Immune Modulation
Gut microbiota influence immune system function, affecting susceptibility to autoimmune disorders and neuroinflammatory conditions. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can disrupt immune homeostasis, potentially exacerbating neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease.
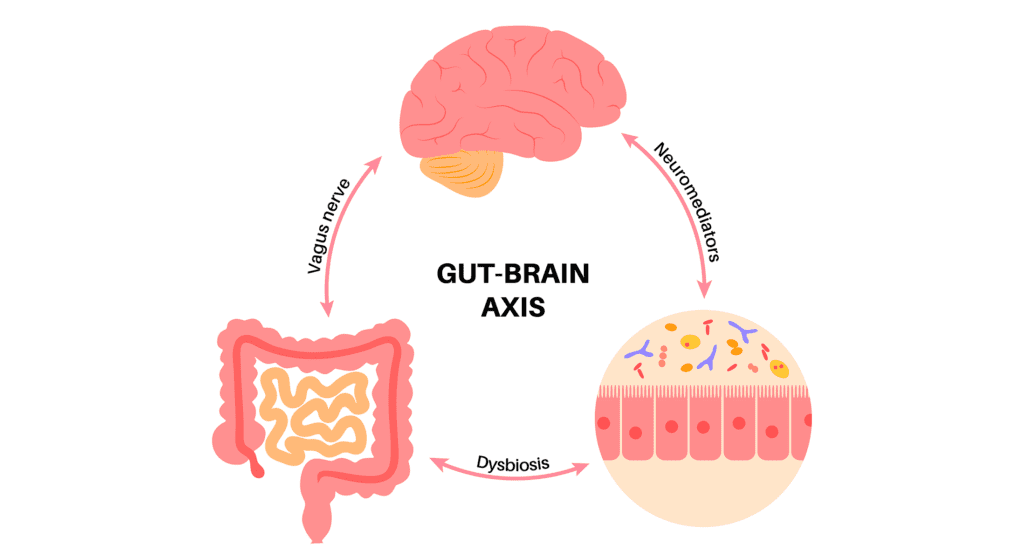
How does gut health affect brain health?
The profound influence of gut health on brain function involves intricate pathways and interactions:
1. Neurotransmitter Production
Gut microbes produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which play crucial roles in mood regulation, stress management, and cognitive function. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters due to dysbiosis can contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
2. Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota supports the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, a protective barrier that regulates the passage of molecules between the bloodstream and the brain. Disruptions in gut health can compromise this barrier, potentially increasing the risk of neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.
Why is the gut-brain axis important to understand?
Recognizing the interconnectedness of the gut-brain-bone axis has profound implications for holistic healthcare:
1. Holistic Approaches to Healthcare
Integrating gut health considerations into healthcare protocols allows for comprehensive management of orthopaedic conditions, neurological disorders, and overall well-being. By addressing gut health through personalized dietary recommendations, probiotics, and lifestyle modifications, healthcare providers can optimize patient outcomes.
2. Prevention and Disease Management
Understanding the impact of gut health on multiple bodily systems enables early intervention and preventive strategies. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, individuals can potentially reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases associated with inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.
Conclusion
The evolving understanding of the gut-brain-bone axis highlights its significance in maintaining optimal health across the lifespan. By fostering a balanced gut microbiota through proactive measures and evidence-based interventions, individuals can support musculoskeletal integrity, cognitive function, and overall quality of life.
As research continues to unravel the complexities of this interconnected system, healthcare providers are poised to implement innovative strategies that harness the therapeutic potential of gut health. Through collaborative efforts in research, education, and patient care, we can harness the transformative power of the gut-brain-bone axis to promote lifelong health and vitality.
Know More About The Gut-Brain Connection: How it Works and The Role of Nutrition
Gut Health and Joint Inflammation: Exploring the Connections
